Tread Pattern Engineering: Reducing Noise Through Design and Simulation
Date: 27 August 2025
In today’s evolving transport network, efficient and safe driving is of utmost importance. Vehicles are also bound to maintain regulatory compliance and reduce noise, air, and other environmental pollution.
Tread pattern design plays a critical role in tyre noise reduction. This tyre design engineering controls the interaction between the tyre and the road surface. Therefore, this design plays a crucial role in reducing air and noise pollution.
Furthermore, tread pattern design adds a higher level of safety to vehicle tyres, providing overall road safety to drivers in different environments.
Read to learn how efficient tread pattern design helps with noise reduction.
Understanding Tread Pattern Engineering
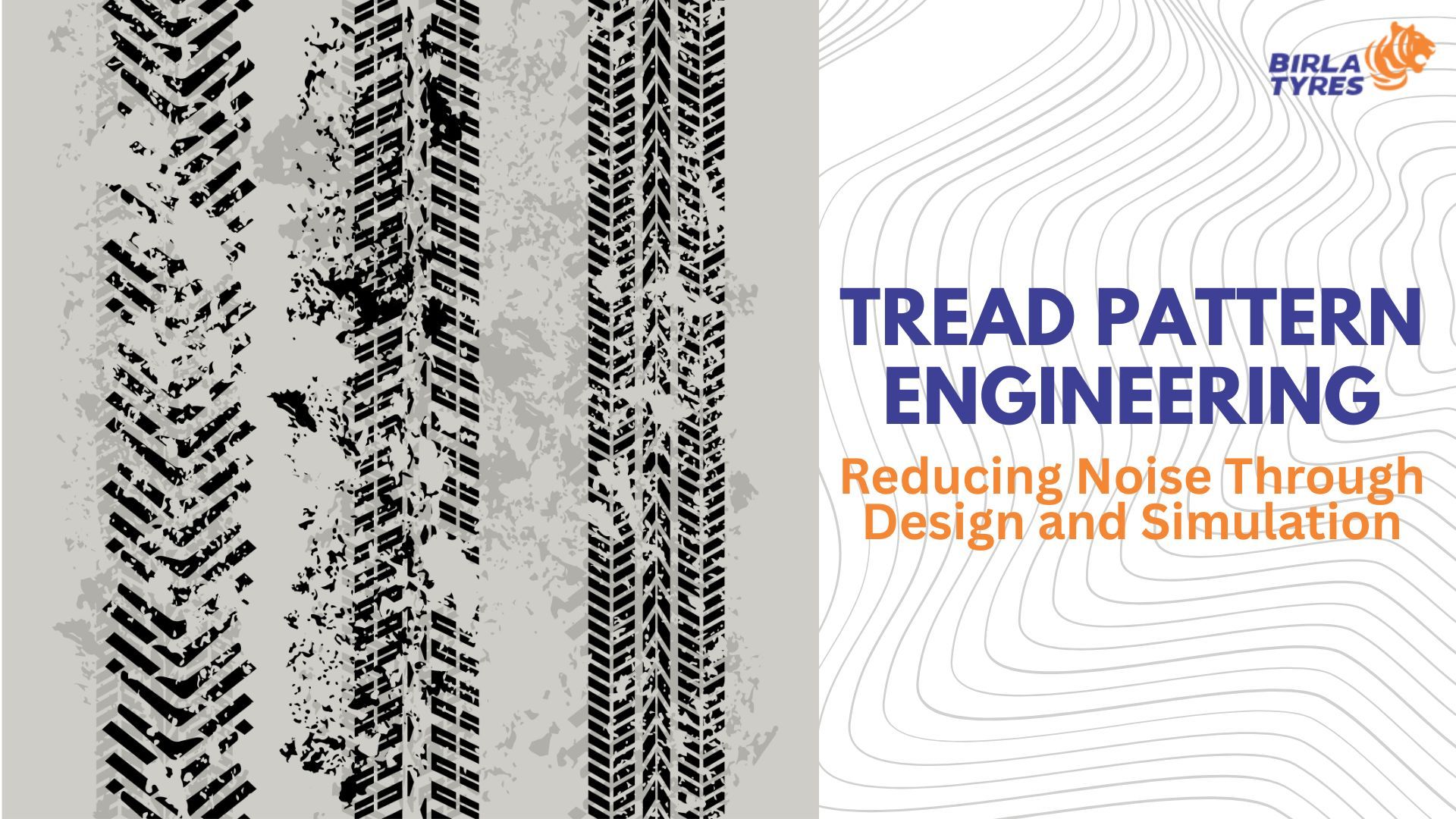
Tread pattern design is both the art and the science behind how engineers build tyres. It’s the technique to design the raised rubber segments, grooves, and sipes on the surface of the tyre.
Designers manipulate the geometrical design patterns on the tyre, and the use of compounds helps them fine-tune the grip, durability, and handling of the tyre. This design process makes the tyre efficient for wet weather, helps with tyre noise reduction, and contributes to efficiency.
However, it’s critical to remember that the performance and efficiency of tyres also depend on the tyre depth, tyre structure, material composition, and inflation pressure. For more information on tyre anatomy and patterns, read this tyre guide.
Different Components of Tread Pattern Engineering

The following are the different components of tread pattern engineering:
- Tread Blocks: Tread blocks are the raised rubber segments that directly contact the surface of the road. The raised sections of the tyre provide the primary point of contact with the road, ensuring better traction and grip.
- Ribs: Ribs are also raised sections of the tread pattern. Typically, these are made using a connected series of treat blocks. These sections of the tread pattern ensure stability of the steering wheel when the driver is taking turns or cornering.
- Grooves: Grooves are a series of deep channels running circumferentially between the blocks and the ribs of the tread pattern. These channels exist to evacuate water from the contact patch of the tyre. It’s an essential safety-focused engineering to prevent hydroplaning.
- Sipes: The surface of the tread blocks has small, thin slices of cut moulded inside. These are tiny slices and slits on the tyre creating "biting edges" helping the tread with additional grip, especially when the vehicle is going through slippery surfaces such as wet or icy roads.
Types of Tread Patterns
Tread patterns come in three different categories:
- Symmetrical: Symmetrical tyres feature the same design across the entire tyre. These are efficient tread pattern designs for vehicles that need more speed, efficiency, and prioritise road safety.
- Asymmetrical: A combination of different tread designs makes asymmetrical tyres efficient for better road-holding capabilities. Despite the road conditions, the tyre provides efficient grip and control.
- Directional: Directional tread patterns take a V-shaped design rolling in one direction. This type of design is ideal for high-speed performance and excellent water drainage.
What is the Goal of Tread Pattern Tyre Design?
Tread pattern tyre design helps a vehicle achieve more than efficient driving. It provides a combination of optimal grip, handling, ride comfort, fuel efficiency and noise reduction.
However, types of tread pattern design vary depending on the performance requirements of a vehicle. For instance, bus and truck tyres require heavy performance and optimal grip and handling.
How Tread Patterns Help with Tyre Noise Reduction?
The following are the ways through which tread patterns help with tyre noise reduction:

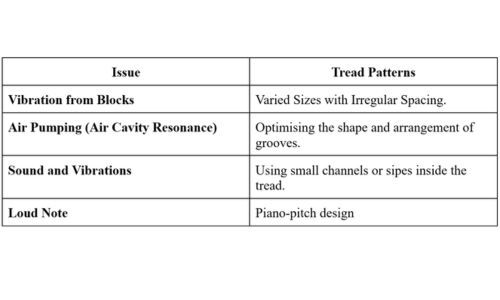
1. Vibration from Blocks
Large, uniform blocks of the tyre create a consistent and high-frequency noise when the vehicle is on the move. Engineers design patterns and blocks to counteract this.
Engineers prevent vibration from the blocks by using varied sizes of irregular spacing. It allows them to break up the pattern and help absorb the shock and repeated impacts.
2. Air Pumping (Air Cavity Resonance)
When the tyre rolls, the grooves and the channels in the tread pattern function like air pumps. Unevenly shaped and sized grooves create and amplify sound waves, and lead to noise. Engineers optimise the shapes and the arrangement of the grooves to minimise the air pumping effect.
3. Sipes and Channels
Small channels or “sipes” inside the tread help create quiet tires. These ensure a more peaceful ride and minimise vibrations by providing a smooth contact with the road.
4. Piano-Pitch Design
Piano-pitch design requires designing the tread pattern so that the blocks and the grooves repeat at irregular intervals and/or "pitches". This arrangement randomises the frequencies produced through the friction.
Therefore, piano-pitch design is efficient in preventing the build-up of a loud note. This way, the tyres create a smoother and quieter sound, thus ensuring top-end tyre acoustics.
Design Elements for Noise Reduction
Manufacturers pay attention to different design elements for tyre noise reduction at the manufacturing level. These design elements are essential to tread pattern engineering.
1. Variable Tread Widths
Manufacturers avoid discrepancies in design by using computer simulations and arranging blocks of different widths. It’s good for avoiding uniform frequencies.
2. Optimised Pitch Sequences
The arrangement of different block lengths and spacing gets optimised to reduce unwanted noise frequencies.
3. Tread Block and Groove Design
Blocks, smaller in size and tightly packed, are used with thoughtfully shaped grooves to minimise contact noise and air pumping.
4. Symmetrical Patterns
Some designers use symmetrical patterns alongside sipes to facilitate a smooth ride and reduce noise.
How Does Tread Pattern Design Work?
Tread pattern engineering for tyres helps achieve other benefits aside from reducing noise. Engineers create these design patterns to create different footprints on the road and tailor them to different driving environments.
- Water Evacuation: Aside from tyre noise reduction, grooves of the tread pattern engineering channel water away from the tyre’s contact patch. Therefore, it improves the grip and prevents aquaplaning.
- Traction: The arrangement of tread blocks and sipes is created to provide mechanical grip on different surfaces. Whether it’s a dry road, muddy path, or snowy highway, the vehicle cuts through efficiently, thanks to the design of the tyre.
- Handling & Stability: Manufacturers create complex patterns to offer cornering stability and precise vehicle handling.
- Durability & Comfort: Reducing the wear and tear on the tyres is just as important, which is why some designers focus on creating tyres built for a longer shelf lifespan. Thanks to their durability, these tyres also provide a comfortable driving experience.
- Specialised Needs: Different patterns are engineered for different applications. Aggressive off-road blocks help with off-road driving. On the other hand, deep groves are great for winter. Racing bikes, on the other hand, need minimal patterns to maximise contact during high-performance drag races.
Birla Tyre Tread Pattern Design for Noise Reduction
Birla Tyre is efficient in reducing tyre noise through advanced engineering. It creates an asymmetrical tread pattern with different block sizes, pitch sequences, and grooves. The purpose of these tyres is to disrupt airflow and prevent resonance.
1. Careful Tread Pattern Engineering
Some specific designs can include continuous circumferential ribs, sipes, smaller tread blocks, and a multi-cavity structure inside the grooves. These tyres intend to minimise noise at the source by avoiding harmonic frequencies responsible for sound when the tyre and the road interact.
2. Asymmetrical or Random Pitch Patterns
Different sizes and spacing of tread blocks and grooves create different pitch patterns. It’s efficient in disrupting the consistent vibration that causes noise.
3. Smaller and Tightly Packed Blocks
Large aggressive tread blocks typically create more noise. On the other hand, smaller and densely packed blocks make tyres quieter.
4. Continuous Ribs and Straight Grooves
Circumferential ribs coming with straight grooves or a series of continuous grooves provide a smooth and quiet ride. It also minimises road surface noise.
5. Sipe
Small slits or the sipes of the tread pattern design help break airflow and reduce tyre noise.
6. Groove Design
The shape and placement of grooves affect airflow and air column resonance. Advanced designs include different features such as multi-cavity structures, or convex/concave within the grooves to absorb sound energy.
7. Reinforced Shoulders
Reinforcing the tread blocks, especially at the shoulder, improves stabilisation. It leads to a quieter and more controlled driving experience.
Example: Birla S49+
Birla S49+ scooter tyre has a low-knob pattern. The unique groove design that it comes with is efficient at evacuating water. It’s efficient for promoting comfort and a quiet riding experience. This combination of supple tread with reinforced sidewalls contributes to superior grip and improved noise reduction.
Engineering and Simulation Strategies
Birla Tyre uses finite FEA and high-fidelity simulation tools. It allows them to optimise the tread patterns of the tyre to improve performance, fuel efficiency, and simulate complex tyre-road interaction.
This engineering and simulation involves using different software such as Creo Parametric to model different designs and evaluate the performance, focusing on metrics such as deformation, stress, and grip.
1. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
The following are some of the major aspects of finite element analysis:
- Purpose: Finite Element Analysis allows for stress analysis and the deformation in the tyre under loading and unloading conditions. It helps with the identification of the best design for better grip and durability.
- Process: Once the tread patterns and the tyre are modelled using 3D software such as Creo Parametric, the model is imported into the FEA solver (like ANSYS). It helps perform the analysis.
- Outcome: A comparison between different tread patterns, FEA helps with determining the design that offers the best grip. It’s essential for the best grip, low stress, and very minimal deformation.
2. High-Fidelity Simulation
Here are the purpose and focus areas of high-fidelity simulation:
- Purpose: High-fidelity simulation helps predict and analyse complex tyre-road interaction in different scenarios. This type of testing leads to better product performance in the long run, providing durability and safety.
- Focus Areas: The simulation helps predict road-load capacity of the vehicle (the tyre), therefore, ensuring improved fuel efficiency through precise modelling of tyre behaviour.
3. Performance Evaluation Metrics
The performance evaluation metrics depend on the following aspects:
- Stress & Deformation: FEA helps find out the most durable and robust tread patterns by measuring stresses such as deformation under different loading scenarios.
- Contact Pressure & Friction: Simulations analyse contact stress and pressure at the junction of the tyre-road interface. Thereby, it ensures optimal grip and performance.
- Noise Reduction: Adjustment of the shape of tread elements is also implemented to reduce pattern noise and make the driving experience more comfortable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The following are some of the most common questions about tyre noise reduction:
1. How Tread Patterns Help with Tyre Noise Reduction?
The following are some of the ways through which tread patterns help with noise reduction:
2. What Are the Design Elements for Noise Reduction?
The following are the design elements for noise reduction:
- Variable tread widths
- Optimised pitch sequences
- Smaller and tightly-packed blocks
- Symmetrical patterns
3. How Does Birla Tyre Tread Pattern Design Help in Noise Reduction?
Birla Tyre tread designs help with noise reduction in the following manner:
- Careful tread planning and engineering
- Asymmetrical or Random pitch patterns
- Smaller and tightly-packed blocks
- Continuous ribs and straight grooves
- Using sipes in tread patterns
- Multi-cavity groove structures
- Reinforcing tread block shoulders
Drive with No Noise!
The use of advanced engineering and simulation strategies at Birla Tyres has helped us create a smooth and noise-free driving experience. The use of tread pattern engineering and simulations in affiliation with Birla Carbon empowers us to build a comfortable and safe driving experience.
Birla Tyres uses advanced engineering and simulation strategies, particularly through its affiliate Birla Carbon. High-fidelity modelling and virtual testing are key to creating high-performing and safe tyres. Tread pattern engineering at Birla Tyres makes every mile count with a quiet and steady driving experience.